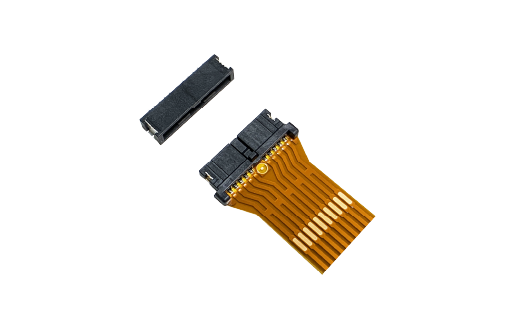
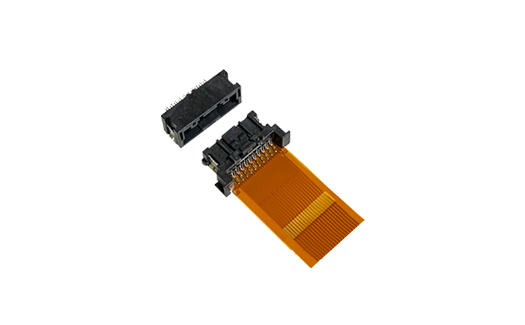
CF1 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connector
Lightweight 50 V DC Connectors Suitable for Harsh Automotive Applications with High Shock, High Vibration, and 125°C High Heat Resistance Requirements
The demand for FPC cables within automotive devices is increasing, such as instrument panels, steering switches, rear lamps, shift levers, side mirrors, headlamps, and battery management systems. Automotive applications have a growing trend to reduce the overall weight and avoid operator wiring failures caused by electrical wire connections.
Panasonic has developed the CF1 Series Board-to-FPC solution for this purpose. The CF1 Series Board-to-FPC connection has a 125°C heat resistance and necessary vibration characteristics suitable for the automotive and transportation market. A significant benefit is that these new Automotive Connectors can be directly connected without requiring any relay wiring harnesses when connected with FPC cables and boards for battery management systems. Panasonic's CF1 Series Automotive Connectors preserve contact reliability using a double-sided clip contact structure.
Panasonic's CF1 Series Connectors have an Inertia lock construction to prevent half-mating for the 4-pin type. An "anti-misoperation bridge structure" also contains the unintended operation of the mating lock. The CF1 Series design also allows reflow soldering of the plug assembly to be performed simultaneously with other Surface Mount Devices without other processes where competing devices require a manual connection.
Feature and Benefits
- Number of Pins: 4, 6, 10
- Rated Current: 2.0A/Pin Contact
- Rated Voltage: 50 V DC
- Heat Resistance Up To 125°C and Strong Mechanical Shock and Vibration Resistance Using Double-Sided Clip Contact Structure
- Suitable for Harsh Automotive Applications That Require High Shock, High Vibration, and Ability to Withstand High Temperatures
- Simple and Lightweight Solution and Easy FPC and Board Connections Without Relay Wiring Harnesses
- Reflow Compatible for Simplified Assembly Process
- Anti-Misoperation Bridge Structure Prevents Unintended Operation of Mating Lock
CF1 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connectors Features and Benefits
- Number of Pins: Available in 4, 6, and 10 pin configurations
- Rated Current: 2.0A per pin contact
- Rated Voltage: 50 V DC
- Heat Resistance: Up to 125°C, suitable for high-temperature environments
- Shock and Vibration Resistance: Designed to withstand strong mechanical shocks and vibrations
- Double-Sided Clip Contact Structure: Ensures strong and reliable connections
- Lightweight and Simple Solution: Easy FPC and board connections without needing relay wiring harnesses
- Reflow Compatible: Simplifies the assembly process by allowing simultaneous reflow soldering with other surface mount devices
- Inertia Lock Construction: Prevents half-mating and unintended operation of the mating lock for the 4-pin type
- Anti-Misoperation Bridge Structure: Prevents unintended operation of the mating lock
Part number list
Resources
Playlist

NPI: CF1 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connectors
New Product Brief: CF1 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connectors

New Product Introduction: CF2 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connectors

CF1 and CF2 Automotive Connectors
CF2 Series Board-to-FPC Automotive Connectors

Panasonic Automotive Solutions for Electrified Drivetrain

Panasonic Automotive Solutions for ADAS