Relays Replacing Contactors
Published on- Relays & Contactors
Relays and contactors are electrically operated switches intended for both switching of loads and controlling electrical circuits. Functionally, relays and contactors fulfill the same role in a circuit which is to provide isolation between a control circuit and an output circuit. Inherent advantages such as small size, PCB mount capability, and low cost allow engineers to replace contactors with relays in several applications.
Relays vs Contactors
Relays and contactors fulfill the same role in a circuit by providing isolation between a control circuit and an output circuit. With essentially the same functionality, there are inherent similarities. Both components use a coil on the input side which creates an electromagnetic field to open and close contacts on the output side. They both come in various arrangements, including normally open and normally closed contacts with multiple poles. However, there are also key differences in these technologies, which have led engineers to start replacing contactors with relays.
Contactors are typically designed for carrying or switching large loads, and therefore are larger in size and often include features such as spring-loaded contacts to help ensure the contacts separate when de-energized. Without this feature, the high heat generated from a large carry current may weld the contacts shut. These spring-loaded contacts also require a higher amount of energy to keep closed in comparison to the smaller hinge spring found in most relays.
Contactors may also employ magnetic arc suppression which blows the electrical arc travel distance along an insulated wall to safely extinguish during contact breaking. This feature is only found in a limited number of relays that are specifically designed for high current cut-off applications.
Advantages of Relays
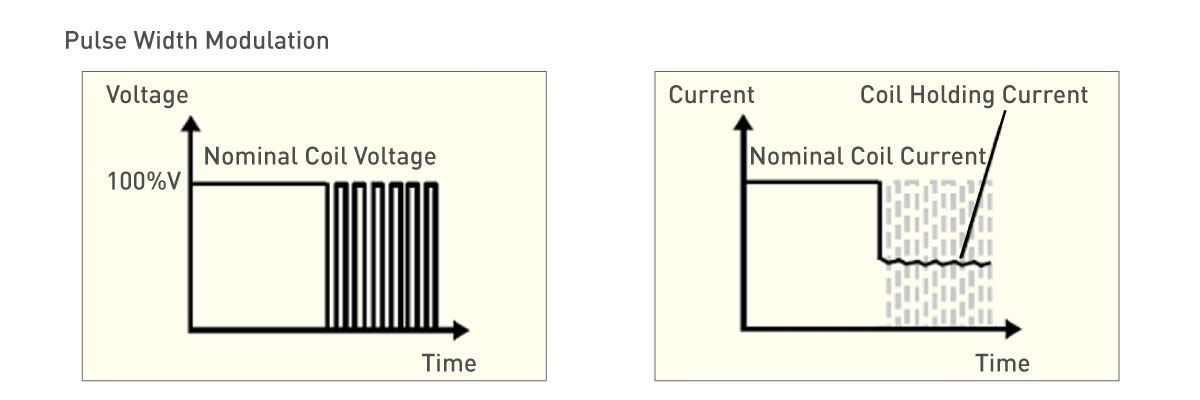
Relays are generally designed for smaller resistive and inductive loads and are therefore smaller in size. Since relays are smaller, they use less valuable board space and tend to cost less. Using wide blade terminals, relays can still carry high current while being able to be mounted directly on the printed circuit board (PCB). This makes for an easier assembly process without requiring screw terminals which is critical for high volume projects where boards need to be produced quickly. The smaller armature design also allows for lower coil operating voltage and in some cases, low coil holding voltage implemented through Pulse Width Modulation. This in turn results in less overall power consumption in the end application.
There are some limitations of relays that should be considered during design, including the ability to switch higher capacity loads that may still require the larger size of a contactor. In general, contactors tend to list more inductive ratings for motor loads, lamp loads, and capacitive loads than relays. Relays tend to have a lower short circuit current capability. Contactors are also often provided with normally closed auxiliary contacts that can be used to monitor if the main normally open contacts have welded. This feature is less common in relays.
HE SERIES RELAYS PV TYPE
Panasonic's HE Series Relays PV Type is available in three different contact ratings: 35A, 48A, or 90A. These relays have a 1 Form A (SPST-NO) contact arrangement in a PC Board mountable small case size. The HE Series Relays feature the minimum contact gap and 2.5kW surge breakdown required by photovoltaic standard requirements
HE-N SERIES RELAYS
Panasonic's HE-N Series General Power Relays feature high switching capacity of 120A @ 480VAC or 55A @ 800VAC in a 1 Form A (SPST-NO) contact arrangement. Offering a compact size of 50mm x 40mm x 43mm, HE-N Relays can be mounted on a PC Board without screw terminals for easier design and faster board assembly.
HE-S SERIES RELAYS
The HE-S Series is a compact Power Relay with low operating power and high-capacity switching. This relay features contacts with long electrical life and a high-capacity resistive switching load rating of 35A at 277VAC for 50,000 cycles. This relay also features a mirror contact structure (compliant with EN60947-4-1) which uses a 2 Form A coupled with a 1 Form B contact arrangement.
Panasonic has been developing PCB-mountable relays as AC Contactor solutions that address all these shortcomings to fit into emerging markets. The HE PV Series relay can carry up to 90A, while the HE-N Series is rated for up to 120A. These higher current ratings are ideal for inverters and single-phase Level two chargers typically found in North America. The Panasonic HE-S Series relay comes with two normally open contacts each rated for 40A at 277VAC and also contains one normally closed auxiliary signal contact to detect contact welding. There are several applications where engineers are beginning to consider using relays instead of contactors, including electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) and charging stations, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and solar and industrial inverters. In these applications, the relay is used as a safety cut off for AC power. In short, relays are typically smaller in size, less expensive, lower power, PCB mountable, and now available with high carry and switching current capability.